Water - an amazing element, some it attracts and fascinates, while others repels. There are also people who experience panic in front of water. Hydrophobia is considered a fairly common type of pathological fears.
Description and variations
Hydrophobia or aquaphobia (both names are equally valid) - it is a mental disorder manifested in an irrational fear of water. The doctors of antiquity paid attention to the fact that people and animals with rabies show signs of hydrophobia, because of this, the fear of water for a long time was called rabies.
Later, a deadly infectious disease caused by a virus of the Rabies genus, nevertheless, was proposed to be separated, and the name “rabies” remained with it. A mental disorder associated with hydrophobia, has become known as hydrophobia.
Fear of big water, in general, is peculiar to humanity, because water not only makes it possible to survive in a physiological sense, but also is capable of taking a person’s life. therefore This phobia is usually attributed to the ancients, directly related to the work of the deepest parts of the brain that have survived since the dawn of mankind, the limbic system.
Since the sources of water and its appearance may be different, then There are quite a few types of fear. These include the fear of drowning, the fear of the bathing process. Some are afraid only to enter the water or swim, but they can calmly contemplate the waters and the sea.
Some without shudder can not even look at the pond. Hydrophobic can be afraid of big water - the sea, lakes, rivers (most often people do not know how to swim), and can be horrified by the type of water in a bath or glass. Sometimes fear suggests the need to swallow water, drink. Some are afraid of clear water, while others - muddy. Some are terrified by cold water, others - hot. There are aquafhobes who fear everything at once.
Some are afraid only in situations where they are in the vicinity of water or in water, others are constantly worried because water surrounds us everywhere - at home, on the street, on vacation and at work.
Psychiatrists had long doubted whether this fear was considered a disease, and therefore in 1940, when the “Psychiatric Dictionary” was compiled, hydrophobia was not included in it. But the omission was corrected in 2004, when the lists of mental illnesses for the eighth edition were revised. And today such a diagnosis exists, it is listed in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) under the code F-40 (phobic mental disorders).
For a mental disorder characteristic is uncontrollable fear that is beyond the power of common sense and willpower. Hydrophobic understands perfectly well that his fear is ridiculous, unjustified (what is terrible in a glass of water?), But he cannot cope with himself as soon as he gets into circumstances or a situation that seems dangerous to him (even if it is just a necessity to drink a glass of water ).
Do not confuse hydrophobia with panic fear of depth. Fear of deep water is called bathophobia, and it is more widespread (up to 50% of people on the planet are more or less afraid of depth). However, bathoboty fear only depth (this is a kind of spatial phobia), you will not frighten them with water in a glass or basin.
This aquafob often does not remember when he first had fears associated with water. Some believe that they were born with such a feature. Often the fear of water or circumstances and actions associated with it is accompanied by obsessive thoughts (obsessions), and sometimes compulsive disorder (the need to perform certain actions, rituals).
Hydrophobia is an independent disease, and sometimes it is only one among other symptoms of mental illness, for example, in bipolar disorder or schizophrenia.
History knows a lot of famous hydrophobes. This fear suffered an American actress Natalie Wood All her life she was afraid of open natural reservoirs and eventually sank off the island of Santa Catalina in California.
Afraid of water Hollywood diva Michelle Pfeiffer, singer and model Carmen Electra. In ancient times, the Byzantine emperor suffered from hydrophobia. Heraclius the First. As a result, he became a hostage to his fear and received several crushing defeats from the Arabs just because he couldn’t decide to cross the Bosphorus during a tactical retreat.
Afraid of the water and Woody Allen. American actor and film director in his fear has reached the extreme limit - he has several phobias at the same time, obsessive-compulsive syndrome.
Causes of
Hydrophobia may appear and develop in childhood and in adulthood. In children, the cause can be a negative experience, for example, water getting into the ears and eyes, if the child fell in the bath, swallowed water. Subsequent bathing may already be accompanied by protests, which parents often take for self-indulgence and ordinary moods, without attaching proper importance to this. Not being resolved, the problem of the child is aggravated, persistent hydrophobia is formed.
The basis of any type of hydrophobia is a natural component - the instinct of self-preservation. To be afraid of water within reasonable limits is normal. This does not allow us to thoughtlessly dive anywhere, which means it increases survival. But hydrophobia is abnormal because the manifestations of fear are hypertrophied, a person cannot control them.
Most often, in the opinion of psychiatrists, a certain situation lies in the basis, which turned out to be traumatic for the psyche, for example, unsuccessful swimming, awkward and incorrect attempts to learn how to swim, getting into the zone of natural disaster (floods), saw a film about such situations, which left an indelible mark on the psyche.
If this happens in childhood, then the likelihood that the fear will be fixed and become habitual is higher. The adult psyche is more resistant to such events.
It is not necessary that the person himself saw or became involved in stressful events related to water. Perhaps he heard about something that left a mark in the subconscious, for example, he learned that someone familiar to him drowned. Also, the child can copy the model of parental behavior - if a mom or dad is afraid of water, then the likelihood that a child will suffer with exactly the same phobia increases significantly.
Hydrophobia contribute to the nature and personality for example, most often this phobia develops in people who are suspicious and anxious, worrying about anything, impressionable, unable to withstand stress. For such people, not only personal or other people's experience, but also mystical experience may well become the starting mechanism for the development of mental disorder - the fortune-teller predicted death from water, the horoscope does not recommend contact with the water element, etc.
Symptoms
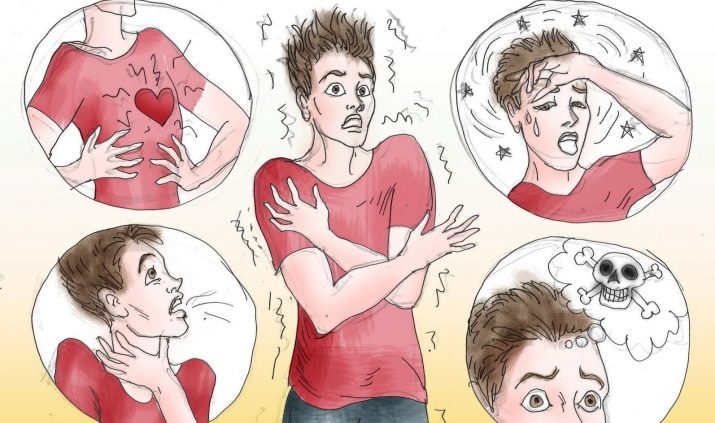
Symptoms that are characteristic of hydrophobia are also characteristic of most other phobic disorders. They can be divided into two groups - psychological and vegetative.
Psychological. Before a water related event should take place, a hydrophob may experience anxiety, which gradually increases, develops, and may disturb sleep and appetite. There are obsessive negative thoughts that revolve in the head, anxiety increases. At the time of a sudden hit in a frightening situation (for example, a hydrophobe pushed into the water or poured over with water) a panic attack is possible.
With her, the patient completely loses the ability to control her behavior, the situation around her. It is for this reason that many aquafhobes drown, even if they can swim, suddenly being in the water.
- Vegetative. If the situation is recognized by the brain as dangerous, there is a sharp rush of adrenaline. Physical symptoms are associated with this: dizziness, weakness in the legs, jumps in blood pressure, abrupt performance of cold sweat, discomfort in the stomach, sometimes nausea and vomiting. Breathing becomes shallow, shallow, pupils dilate, tremor appears. Possible loss of consciousness, balance.
After a panic attack, a person feels tired, devastated. He is very afraid of becoming the object of public condemnation if the attack recurs in public. Therefore, aquafhobes begin to avoid situations in which this can happen.
And here it all depends on the type of phobia. If a person is afraid of reservoirs, it is unlikely that you persuade him to go to the river or spend a day at the beach. If there is a fear of water as a whole, the hydrophob can refuse to wash, replacing it with dry wiping or neglecting hygiene at all.
The most dangerous is the condition in which a person cannot drink water - when trying to swallow, a laryngeal spasm occurs. In this case, he may die of thirst if he is not treated on time.
What is the connection with rabies?
As already mentioned, hydrophobia is characteristic of people infected with rabies, but it acts as a separate symptom. Self hydrophobia is not fatal, it is not interconnected with a dangerous viral disease.
When a person is infuriated, he is thirsty, but he cannot take a sip of water because of a spasm that appears in the throat and larynx at the sight of water, at the sound of water noise. From the moment hydrophobia appears after the bite of an animal until the end of the disease, it takes from one to three days, rarely patients with rabies live more than 5-6 days. After the active phase, coma and death from paralysis of the heart muscle or bulbar centers occur. To date, there is no data on the safe recovery of at least one patient with developed rabies.
With the usual water-related phobia, a person is not aggressive, his life as a whole is not in danger. With isolated hydrophobia, you can live a lifetime, however, the quality of life will not be the highest.
Treatment methods
Treat hydrophobia psychiatrists and psychotherapists. The main method today is psychotherapy. But in some cases, medications are also prescribed as additional treatment - mainly antidepressantsIf anxiety is increased, there are signs of depression. On their own, any medication brings only temporary relief, the root cause remains, fear does not go away.
To overcome the fear of water, get rid of it, appeal to the doctor necessarily. Independent attempts under the strict guidance of instructions from the Internet to overcome the fear can drive fear even deeper, as well as cause other mental disorders. Do not be afraid that the patient will be put in the hospital. In most cases, outpatient treatment is enough, visiting a psychotherapist.
The doctor identifies the causes of fear and if they are deep, childish, then sometimes this requires several sessions of hypnosis. After this, the old patient settings regarding fluids are gradually replaced by new ones. The decisive stage is immersion in the environment, that is, the resumption of contact with water, metered, under the supervision of a specialist. Positive therapy projections - this fear can be overcome.
Many people after the course of treatment can even learn to swim.
Hydrophobia in children
Experts believe that the critical age at which children begin to experience the fear of water under traumatic circumstances is the period from 3 to 5 years. It is at this age that parents should watch more closely so that the child does not watch "Titanic" or films about floods.
It is important to pay special attention to the prevention of accidents on the water. Well, if a child has learned to swim before the age of 3, if this has not happened, do not push him off the pier into the water and wait until he swims out. It is better to burn the kid to a good coach in the pool.
If the child already shows hydrophobia, do not disregard it. Silence of the problem does not solve it. It is necessary to show the child to a child psychologist. At the early stage, many phobias are subject to correction by ordinary conversations, explanations, and game therapy.
The disturbing symptoms in children should include the refusal to swim in the river, the sea, the refusal to wash in whole or in part (for example, the fear of washing one's head), and the refusal to learn swimming. If the home conversation does not help, you need to contact a specialist.