Last week was great! Vigorous energy, a lot of ideas and projects, and all doable! Which one of them to take? Without exception, people are sociable, kind and responsive. Life is Beautiful! Inspired soul soars, sings and rejoices! And suddenly, the recession is heavy, muddy, protracted. Hopelessness, depression. So expressed hypomania: from total positive to total negative. The disease has its own symptoms and treatment.
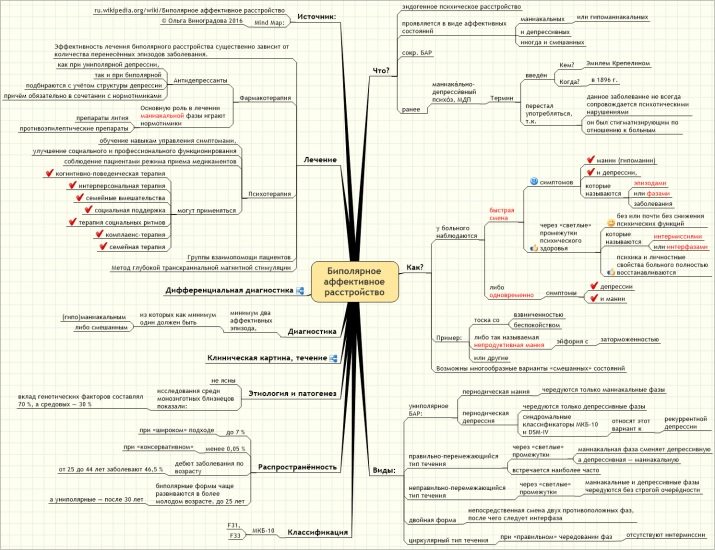
What it is?
Hypomania in psychology - a state similar to mania, but flowing in less mild forms. Manifested in a relatively stable, high spirits, occasionally, on the situation, accompanied by irritation and anger. The condition lasts for several days, manifesting the severity of exhaustive satisfaction, absolute productivity, a high degree of charge and activity.
Differences from mania are lack of psychotic symptoms and increased, sometimes quite productive, efficiency and adaptability. Often it can occur as a phase of bipolar disorder.
In other cases, hypomania functions on the background of failures in the nervous system, hyperthyroidism, psychotropic intoxication, or in the form of side effects when taking certain medications (antidepressants).
In accordance with the ICD-10 formal definition, the state is characterized by an overly positive or irritable attitude, clearly atypical for a specific individual, lasting for at least four days.
In this way, hypomania as an affective disorder is a latent form of mania that occurs in the absence of pronounced arousal. At the same time, there is no obvious behavioral disorganization or deviations from the norms of the social behavior of the individual, since the symptoms of psychosis (delusions, hallucinations, etc.) are not present.
Mood disorders were also observed by Hippocrates (V century BC), who divided them into melancholy and mania. Later, in the works of E. Krepelin, these conditions were attributed to manic-depressive psychosis (TIR).
Conceptually, this definition has been preserved for almost the entire XX century.
Around the 60s of XX century. a number of scientists noted some heterogeneity of the group of states, within which they determined monopolar and bipolar forms. Later, psychologists identified two types of TIR:
- for type 1 characteristic alternation of episodes of depression and mania (sharply elevated mood, leading to serious violations of the functional body);
- for type 2, alternating depressions with hypomanias only (without serious disturbances) are characteristic.
Since 1990, according to ICD-10, 3 degrees of severity of mania - hypomania, mania in the absence of psychotic symptoms, mania with psychotic symptoms - have been distinguished.
It is noteworthy that Ludwig van Beethoven, Virginia Woolf, Ernest Hemingway, Isaac Newton, Judy Garland, Robert Schumann and a number of other geniuses suffered from bipolar disorders.
At one time, doctors diagnosed MH of N. Khrushchev, whose inner circle observed how often his cheerfulness and joy were replaced by deep melancholy.
Traditionally, a disturbed mood is considered episodic, if its duration is about a week.
In hypomania, most people who experience the disorder do not consider themselves to be sick, and therefore do not go to doctors. It is for this reason that reliable statistics of the disorder are absent. Unrecognized affective disorder leads to a worsening of the situation.
Beyond the causes of the disorder it is characterized by disorders of both the affective and somatopsychic spheres. An overestimated general tone, a feeling of well-being and excessive optimism correspond to a stable, upbeat mood. Own advantages and eccentricities are exaggerated, ideas of excellence prevail, there is no critical self-attitude.
Disagreement or opposition from the environment provoke anger. In general, the condition, as well as its signs, are characterized by lability.
The process of thinking in such a person speeds up, speech loses its distinctiveness and expressiveness. Inexhaustible energy and a certain dispersedness stimulate the appearance of an emotional uplift during the execution of even mediocre and routine work. Man enthusiastically takes up the implementation of many plans, without thinking about the reality of their implementation.
The patient has a high threshold of fatigue and resistance to significant stress. Decreased need for rest and sleep. At the same time somatic signs may dominate. Possible prolonged nature of the disorder.
In its cyclothymic periods, hypomania proceeds sufficiently clearly, with pronounced ups and downs of mood. In cases of a protracted option is noted endurance affect.
Probable and atypical pictures of the process - the emergence of overvalued formations, obsessions, depressive pain syndromes.
With relatively even manifestations of the disorder, temporary somatopsychological manifestations may occur in the form of vegetative crises, vital fears, asthenia, etc. More often hypomania occurs within the framework of bipolar affective disorder (BAR), where it is usually replaced by depressions, forming either a continuous continuum or cyclicity. The bipolar form of the disorder often differs in its early manifestations (in childhood or adolescence) and in the chronic form of the course, which can be:
- remitting (episode - remission - episode);
- with double phases (one episode is immediately replaced by the opposite direction);
- continual (there are no periods of remission between episodes).
Normal remission occurs in a small number of patients. The disease can turn into a more pronounced state - mania. The average duration of episodes is in the range from 2 weeks to 2 months.
The rhythmic pattern of the occurrence of episodes is characterized by spontaneity, which leads to the patient's feeling of self-doubt.
BAR refers to diseases that cause disability. In addition, with bipolar disorders, the risk of suicide increases significantly.
Varieties
There are several varieties of hypomania:
- simple ("fun");
- irritable or angry, expansive.
Depending on the accompanying personality disorder hypomania:
- querulant (with the patient's irresistible desire for litigation, constantly fighting for “violated” rights);
- adventurous (inclination to adventure);
- dysphoric (irritability, replaced by a feeling of melancholy, tension, tendency to aggressive behavior).
According to the type of influence of hypomania on the somatopsychic sphere, there is also an atypical hypomania (euphoric hypochondria), the flow of which is accompanied by elevated mood and unrestrained activity aimed at overcoming an imaginary ailment.
On the basis of the severity of symptoms emit:
- pure (explicit) form of hypomania;
- hidden hypomania (erased form).
There is also the so-called productive form of hypomania, observed during cyclothymia, characterized by infrequent failures of the “sleep-wakeful” cycle and acceleration of ideator processes.
Causes
The occurrence of hypomania contributes to a number of reasons.
- Excessive activity of the thyroid gland, accompanied by increased hormone production. Contribute to the breakdown of postpartum syndrome and menopause.
- Hypomania episodes also appear as a consequence of the phase of food arousal. The causes may be anorexia or fasting.
- It leads to the disease and taking certain drugs (opiates, baclofen, phenamine, captopril, bromkriptin, bromides, cimetidine, cyclosporine, corticosteroids, yohimbine, teturam, hallucinogens).
- In cases of abrupt withdrawal of antidepressants.
- With excessive use of stimulants (energy drinks, cocaine, coffee, etc.).
- Cases of organic brain damage (infectious and non-infectious nature).
- Bipolar affective disorders (MDP), the occurrence of which is stimulated by hereditary factors and stresses.
How does it manifest itself?
Symptoms of hypomania include:
- atypical for the individual increased irritable mood persisting for several days;
- unusual talkativeness and fast pace of speech;
- increased levels of physical activity;
- reducing the need for rest and sleep;
- distraction of attention;
- manifestations of recklessness and inadequate situational behavior;
- abnormally high degree of sociability and familiarity episodes of communication;
- increase in sexual desire.
Hidden forms of hypomania manifest their appearance by disinhibition (in childhood and adolescence), bulimia, nymphomania and satiriasis. Probably episodes of high creative productivity, accompanied by a feeling of inspiration.
In case of hormonal disorders, an elevated temperature (37-38 °) is added to the previously listed symptoms.
Signs of hypomania caused by hyperthyroidism are tremor and Grefe’s symptom (“the symptom of the setting sun”). Hypomania is often accompanied by increased appetite.
For childhood hypomania characterized by manifestations:
- fussiness and pronounced motor disinhibition;
- impulsiveness;
- disobedience and unusual stubbornness;
- grimacing;
- verbosity;
- inclination to rude antics;
- difficulty falling asleep;
- a sharp increase in instincts and drives (gluttony, masturbation).
Diagnosis and treatment
The main criteria for diagnosing a disorder are the presence of excessively elevated or irritable mood for at least 4 days.
For a reliable diagnosis, tests are used, and at least 3 symptoms from the list below should be identified as necessary and sufficient:
- high level of activity or anxiety;
- excessive talkativeness;
- difficulty concentrating or distracted;
- reduced need for rest and sleep;
- increased libido;
- minor revelings or reckless actions, irresponsible behavior;
- excessive sociability with manifestations of familiarity.
Due to the fact that hypomania is provoked by various reasons, differential diagnosis is carried out in psychiatry. If an episode of hypomania is provoked by the adoption of psychoactive drugs, then signs of intoxication are accompanied by an increase in mood.
The patient has an altered pupil size, tremor and autonomic responses.
In children, the disorder is manifested mainly at the psychomotor level of response, due to the fact that at this age manic states are more atypical than in adults. It is important to bear in mind that for preschool and junior schoolchildren, the cheerfulness, activity, and the lability of a mood, manifested under the influence of many factors of internal and external order, are normative. It is for this reason that hypomania in children is suggested for prolonged euphoria, accompanied by impulsive and gross behavioral disorders.
With such causes of the disorder as hyperthyroidism or intoxication with psychoactive substances, the therapy consists in eliminating these causes (thyrostatic drugs, surgical treatment, etc.).
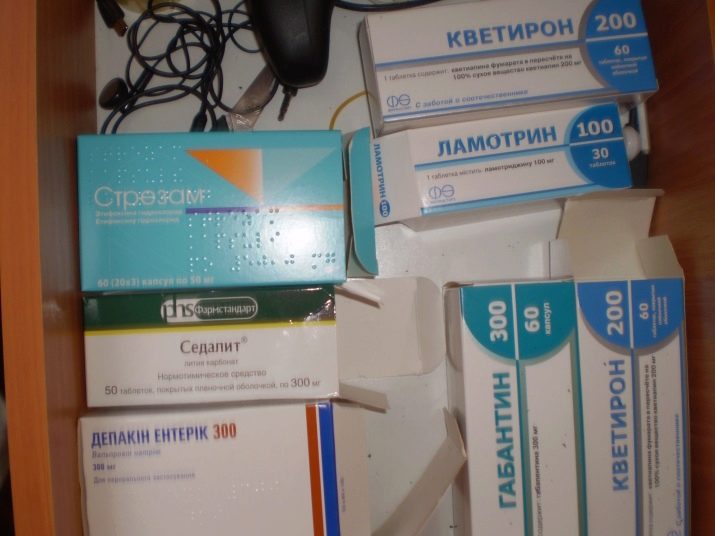
In cases of bipolar disorders use mood stabilizers (mood stabilizers):
- for example, litosan or litobid (the dosage is strictly individual, the smallest dose is 0.6 mmol / l);
- anticonvulsant drugs (valproate, carbamazepine, gabapentin, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, etc.).
The second group of drugs can be used in combination with the first.
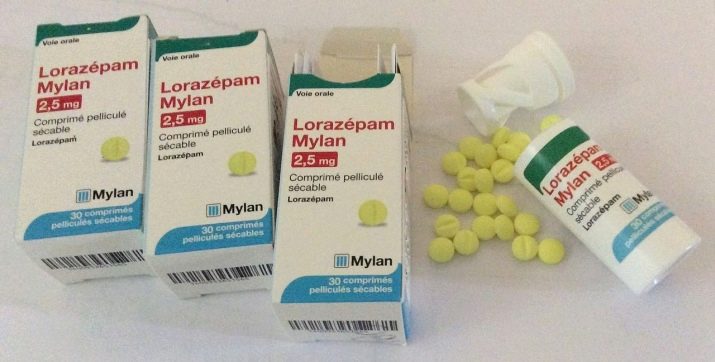
When insomnia prescribed benzodiazipines (clonazepam, lorazepam). Because they are addictive, they are used for a short period of time. Sometimes prescribed sedatives (zolpidem). Children more often prescribed lithium preparations.
Application of valproate needs under close medical supervision. This medicine can lead to hormonal changes in adolescent girls and polycystic ovary syndrome in young women.
For more effective treatment of bipolar disorder, it must be accompanied by frequent replacement of drugs with the direct participation of the doctor. Stabilizing agents can be used for years.
The episode of hypomania is stopped by lithium preparations in small and medium doses.
The support of mood stabilizers is usually carried out in the initial period of stopping, since the prophylactic effect of these drugs is slow. Antidepressants can increase the severity of bipolar disorder. In these cases, the use of the drug is abandoned. In cases where mood stabilizers are not sufficiently effective, include atypical antipsychotics in therapy.
What is dangerous hypomania?
Bipolar disorder with the hypomania phase provides for compulsory treatment, since stable hyperactivity naturally leads to depletion of the body, apathy and deep depressive states. Hypomania is fraught with dangerous consequences.
- Lack of sleep leads to a significant overwork of the body. The level of attention and memory drops.
- Possible overeating leads to obesity and the development of avitominoza. The body's defenses are falling, exacerbated by chronic diseases.
- Periodic apathy complicates self-control and creates additional life problems.
- A series of days of excessive activation is replaced by deep depressive and long enough, up to several months, periods. The neglect of hypomania leads to a breakdown. An adequate perception of reality is violated. A person becomes conflict, which leads him to social isolation.
Hypomania often occurs in creative people. In a number of cases, famous writers, poets, composers, artists for a long time (months) fell into periods of inspiration, creating masterpieces of art. However, the periods of recovery certainly alternated with depressions and a significant decline in strength.
Attempts to regain radiant inspiration by drinking alcohol or drugs, lead to an absolute deterioration of the situation.
On the ten signs of mania, see below.