Fear: what it is, the benefits and harm, the causes and methods of struggle

Fear is one of the very first feelings and conditions that a person begins to experience. According to some reports, even in the womb the fetus is able to fear. Then throughout life we have fears, and often they save our lives, allow us not to make big mistakes. At the same time, fear can turn into a real problem and significantly complicate a person’s life.
What it is?
Fear is an inner emotional and psychological state that is caused by the presence of a real or perceived threat. Psychologists consider it a negative emotion, bright and strong, able to influence the behavior and thinking of a person. Physiologists agree with them, but clarify that This emotion is based not only on a dangerous change in external circumstances, but also on past negative experiences.therefore, fear is a necessary condition for the survival of a species.
A person begins to experience fear in situations and under circumstances that in some way may pose a danger to his life, health and well-being.
It is based on the self-preservation instinct as old as the world. Fear is considered a basic emotion, innate.
Do not confuse fear with anxiety. Although both of these states are associated with a feeling of anxiety, fear is still a reaction to a threat, even if it does not exist in reality. And anxiety is the expectation of possible dangerous events that may not occur, since it is difficult to predict them.
Fear allows you to survive, which is why people, whom nature has cheated on its wings, are afraid of heights. Since a person lacks natural armor and the ability to survive without oxygen underground, we all, to one degree or another, are afraid of earthquakes, natural disasters and catastrophes.
To experience fear is a normal reaction of a healthy human psyche, since it can keep a person from actions and actions that can lead to death.
Fear evolved with people. And today we are no longer afraid that at night a tiger or a bear will attack us, but sometimes we are afraid of hysterics to be left without a mobile connection or electricity.
Being a defensive mechanism, fear still tries to protect us from things that could disturb our well-being (physical and mental). However, many are still afraid of the dark, because the ancient memory suggests that there may be an unknown threat in it. Many fear depth, absolute silence, death.
Scientists who, at different times, tried to study the mechanisms of fear, discovered several ways in which this basic emotion tries to “reach out” to our consciousness. These are the so-called hormones of fear and stress (adrenaline, cortisol), these are the vegetative reactions that occur when certain areas of the brain are excited, when there is a strong fear.
As long as a person is afraid of real threats, this is a normal, full-fledged, saving fear, which needs to say a big human “thank you”.
But when fear becomes irrational, inexplicable, uncontrollable, a mental disorder develops, which is called phobia.
Today, almost everyone has this or that phobia (their list is for certain unknown, but scientists have already counted about 300 irrational nightmares). Phobias guide human behavior and thinking. And even though he understands that it is stupid to be afraid of a spider the size of a matchhead, because he does not pose a threat, a person cannot do anything with his horror.
Such fears change behavior - FOB tries to avoid circumstances and situations that inspire horror: a social phobia that is afraid of society, closes in a house and lives as a hermit, you cannot drive a claustrophobe into an elevator, he will even go to the top floor of a thirty-story building on foot, a film photographer will never come close to dogs, and his cumpnophob is so afraid of buttons that he never touches them or buys such clothing avoids contact with people who have large bright buttons on their clothes.
Many pronounced phobias need treatment.
There are no completely fearless people. If a person is deprived of this emotion, he will cease to exist very quickly, since he will lose caution, prudence, his thinking will be disturbed. To understand this, it is enough to know what the mechanisms of phobia are.
Benefit and harm
Fear, fear - these are emotions that can both save and kill. In extreme circumstances, when the threat to life is more than real, fear is meant to be saved, but in practice it often leads to the opposite effect. If a person begins to panic in an extreme situation, then he loses control over the situation and external changes, which is fraught with death. Dr. Alain Bombard from France, to prove this, was forced alone to cross the Atlantic Ocean in a flimsy lifeboat.
The conclusions he made speak for themselves: the main cause of death for people in open water is fear, a sense of doom. He refuted the view that the death of shipwreck victims is mainly associated with a shortage of fresh drinking water.
Bombar is sure that it was fear that deprived them of their will and ability to act according to circumstances.
Fears in large quantities can significantly harm the child's psyche. The frightened child is constantly in suspense, his personality is developing with difficulty, he cannot calmly communicate with others, build contacts, empathize and sympathize. Children who have lived for some time in an environment of total fear, often grow out of control, aggressive.
Excessive fear causes teenagers and children sleep disorders, speech disorders. Thinking loses flexibility, reduced cognitive ability. Frightened children are less inquisitive than their more prosperous peers.
Severe panic experienced in childhood under certain circumstances and without being tied to them can become the beginning of a severe long-term phobia that will require medical assistance.
Adults cope with their nightmares more easily, their psyche is less labile, it is less likely to undergo pathological changes under the influence of horror or fear.
But such consequences cannot be completely excluded. If a person has long and often experienced various fears, It is possible that not only phobias will develop, but also more severe mental diseases - a persecution or schizophrenia mania, for example.
In fairness, it should be noted that fear has a positive meaning. This state brings the human body into a “combat” readiness, a person becomes more active, and in a difficult situation it helps to overcome the dangers: the muscles become stronger and more enduring, a highly frightened person runs much faster than a calm one.
What we fear is a kind of our “teacher” - this is how personal experience of danger is formed.
And in situations where a person is faced with an unprecedented threat, an unfamiliar phenomenon, it is fear that takes upon itself the entire responsibility for behavioral reactions. As long as the individual thinks about what is in front of him and how dangerous it can be, fear has already launched the “run” reaction, and the legs, as people say, carry the frightened person away.It will be possible to think about and understand the strange danger later. And now the main thing - to escape.
Scientists identify several roles that fear performs. They are not bad and not good, they are just necessary:
- motivational - fear leads to choose a safer living environment for children, for themselves;
- adaptive - fear gives negative experience and allows for the future to form a more cautious behavior;
- mobilization - the organism works in the “super-hero” mode, it can jump so high and run as fast as no Olympic champion can in a calm state;
- estimated - fears contribute to the ability to assess the danger and choose the means of protection;
- signal orientation - a danger signal arrives and immediately the brain begins to choose how to behave in order to preserve life and health;
- organizational - because of the fear of being beaten with a belt or put in a corner, the child is less bullied and learns better;
- social - under the influence of fears (to be not like everyone else, to be convicted) people try to hide their negative qualities of character, criminal tendencies.
The function of fear is always only one - to protect and protect. And all the roles are ultimately reduced to it.
Kinds
Those who wish to find the only correct classification of human fears will suffer a great disappointment: this classification does not exist, since there are many different classifications. Emotion, for example, is divided according to the following parameters.
By way of appearance (situational, personal)
Situational fright is a feeling that naturally appears when a situation changes (a flood occurred, a volcanic eruption began, a large aggressive dog attacks the person). Such fears are very contagious to others - they quickly spread and cover entire groups of people.
Personal fears are features of his character, for example, a sensitive person can be scared only because someone, in his personal opinion, looked at him with condemnation.
By object (object, thematic, non-objective)
Object fright is always caused by something concrete (snake, spider, etc.). Thematic concerns a wide range of circumstances and situations in which fear may arise. So, a person with horror perceiving height will be equally afraid of a parachute jump and a climb to the viewing platform of a skyscraper (the situations are different, the subjects are the same). Thematic concerns include fear of loneliness, lack of knowledge, change, etc.
Pointless fear is a sudden feeling of danger in the absence of any particular object, object or subject.
On reasonableness (rational and irrational)
It's all pretty simple. Rational fear is real, caused by an existing danger. Irrational (irrational) fear is difficult to explain from the point of view of common sense, because there is no obvious threat. All phobias, without exception, are irrational fears.
By the time of appearance (acute and chronic)
Acute fear is a normal, perfectly healthy reaction of a person to danger, and manifestations of mental disorders (panic attacks). Be that as it may, an acute fright in 100% of cases is associated with a momentary situation. Chronic fear is always associated with some individual personality characteristics (anxious type, suspicious, shy).
By nature (natural, age and pathological)
Many children experience numerous fears, but with age they almost always pass (the fear of the dark and a number of others “behave” this way). Older people are more likely to be afraid of being robbed, getting sick - and this is also natural. Normal fear from abnormal (pathological) is characterized by the fact that it is short, reversible, and does not affect life in general. If fear causes a person to change life, to adapt, if the personality itself and its actions change, then they talk about pathology.
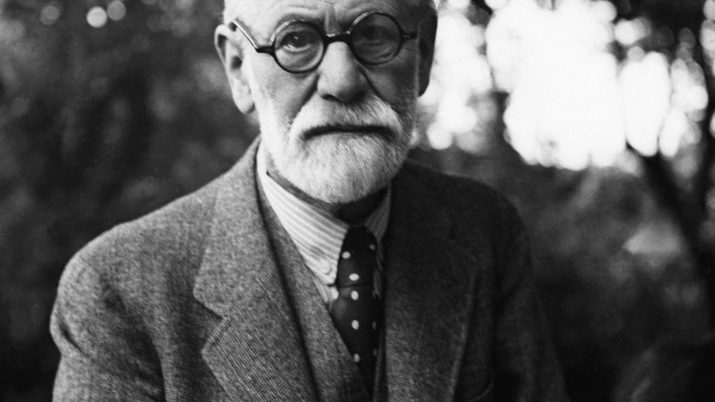
The great psychoanalyst Sigmund Freud, who himself suffered from agoraphobia and was also afraid of ferns, devoted a considerable part of his work to the study of fears.
He also tried to classify them. According to Freud, fear can be real and neurotic. With real, everything is more or less clear, and the doctor did not invent anything new beyond what is already known about the normal reaction to danger. But neurotic fears with the obligatory presence of affect he divided into several categories:
- fearful expectation - foresight, prediction of the worst that can happen in certain situations, in an extremely form the neurosis of fear develops;
- anankastic - phobias, obsessive thoughts, actions, in an extreme form lead to the development of hysteria of fear;
- spontaneous - it is horror attacks without a cause, in extreme form they lead to severe mental disorders.
Modern researchers add to the legacy of the classics of psychoanalysis and psychiatry special species that are the product of civilization. This is a social phobia.
The very circumstances in which they appear are not life threatening, but are still regarded by the brain as a signal of danger.
These are conflict situations in which a person risks losing normal self-esteem, status, and relationships.
Symptoms
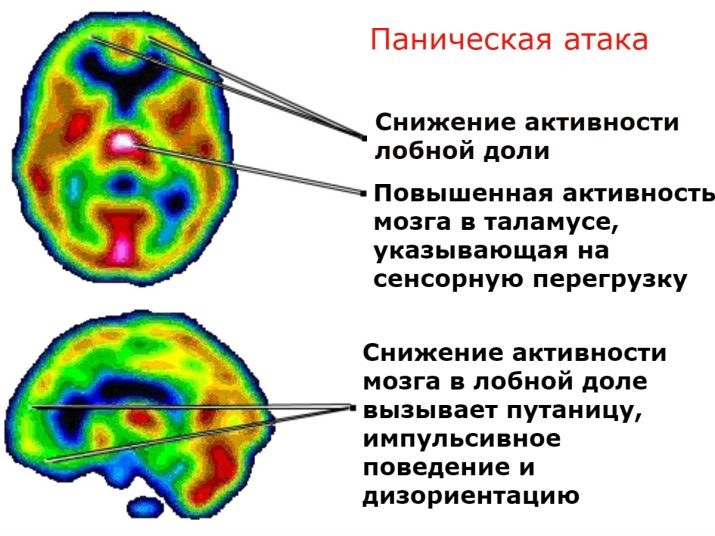
Fear is born in the brain, or rather in the oldest part of it, the central region, called the limbic system, or more precisely, in the amygdala, which is responsible for the ability to make decisions on the results of the evaluation of emotions. Having received a dangerous real or fictional signal, this part of the brain triggers a reaction in which you need to quickly choose what to do — run or defend. Electroencephalography, if at this moment to make such a study, shows the activity of subcortical structures, as well as the cortex.
The human body begins to actively prepare for a fight or escape, it activates the “military” mode needed for this: a lot of blood is sent to the muscles and the heart (you have to run), because of this the skin becomes cooler, the sweat glands become more active and the familiar sign of fear is cold sticky sweat.
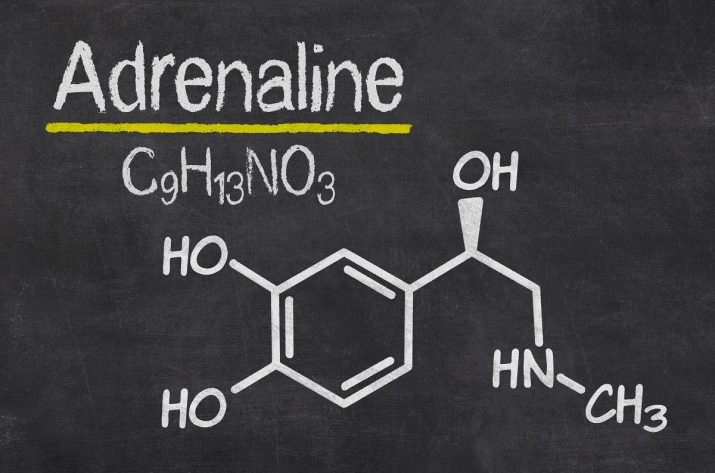
A large amount of adrenaline enters the blood, heartbeat quickens, breathing becomes shallow, superficial and frequent.
Under the action of adrenaline, the pupils dilate (this is what observant people noticed long ago, who came up with the conventional expression that “fear has large eyes”).
The skin becomes more pale. Due to the outflow of blood from the internal organs to the muscle tissue, the stomach shrinks, and unpleasant sensations can appear in the stomach. Often an attack of fear is accompanied by a feeling of nausea, and sometimes vomiting. Severe horror can lead to involuntary relaxation of the sphincters and subsequent uncontrolled urination or bowel movements.
At the moment of fear in the human body there is a sharp decrease in the production of sex hormones (well, correctly - if there is a danger, not time to continue the race!), The adrenal cortex intensively produces cortisol, and the adrenal medulla quickly supplies the body with adrenalin.
At the physical level, with fear, there are drops in blood pressure (this is especially noticeable in adults and the elderly).
Dry mouth, a feeling of weakness in the legs and a lump in the throat (difficult to swallow). Heart palpitations are accompanied by tinnitus, ringing in the head. Much depends on the individual characteristics of the individual, psyche, health.
Panic attacks (panic attacks) are characteristic of people with phobias. A normal healthy mind, even at the moment of fright, will allow a person to control his behavior and condition. With a phobia, control is impossible - fear lives its own, separate life, in addition to the above symptoms, loss of consciousness and balance, an attempt to harm oneself is possible.Horror shackles and does not let go until the end of the attack.
In the case of phobias, a qualified medical diagnosis is required.
The reasons
As can be seen from the mechanisms of development of emotions, the main reason is the primary stimulus. It is noteworthy that even a frightening circumstance that threatens life and well-being, but also the absence of any signs of well-being, can become a cause of fear, horror, panic (such an origin, in particular, has a fear that a young child feels somewhere to go away on their own business).
If there is no security guarantor, it is no less scary than the presence of a real threat.
Human psychology is designed so that regardless of age, education, social status in a society, gender or race, we all fear certain things. - for example, the unknown. If an event does not occur, although it was expected, or it is not at all obvious what should happen next, the person involuntarily brings his psyche to a state of “full alert”. And it is precisely fear that mobilizes it.
In each of us, from birth, the “experience of previous generations” is genetically inherent, that is, the fear of situations that are really highly likely to end badly for us.
That is why, throughout our life, we preserve and transmit to our descendants the horror of natural disasters and fires. Such fear does not depend on the level of culture of the society, on its awareness and technological progress. All other fears are derivatives. A child from an African settlement, in which there is no electricity and the Internet, is unfamiliar with the fear of being left without a mobile phone.
Among the various circumstances causing alarm, fear, researchers especially note such a phenomenon as loneliness.
In a state of loneliness, all emotions are aggravated. And this is not by chance: the prospect of getting sick or getting injured alone increases the likelihood of an unfavorable outcome for a person.
There are both external and internal causes for the development of fear. External are events, circumstances in which life puts us every second. And internal causes are key needs and personal experience (memories, premonition, the ratio of external stimuli to personal experience). External causes can be imposed (people are accustomed to fire alarms, air alarms, etc.). Agree, it is not necessary to see a fire with your own eyes in order to be frightened of it, having heard that a fire alarm system has been triggered in the building where you are.
Personal experience can be different: a person is faced with a danger, has suffered, and the interrelation between an object and the consequences of a collision with it is firmly fixed in his mind.
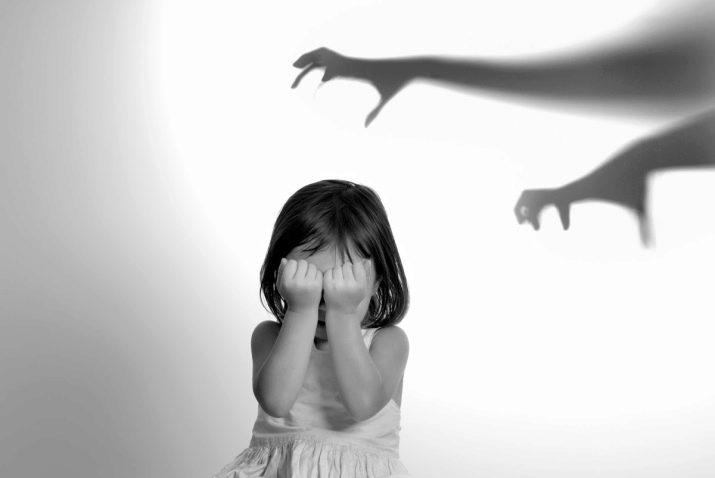
Traumatic experiences in childhood often lead to the formation of resistant phobias even in adults. Often a person is afraid of dogs only because in childhood or adolescence he was bitten by such an animal, and the fear of enclosed space comes after the child was often locked up in a dark closet, storeroom, put in a dark corner as a punishment for improper behavior.
Personal experience may be non-traumatic, based on culture, education, copying. If a child’s parents are afraid of thunderstorms and every time thunder thunders outside the window and lightning flashes, they close the windows and doors tightly and show fear, then the child becomes afraid of thunderstorms, although there was never any physical harm to him directly from thunder and lightning. So people "broadcast" the fear of snakes to each other (although most of them never even met them in life), fear of contracting a dangerous disease (none of them was sick).
The experience that we consider ours is not always the case. Sometimes we perceive statements that are imposed on us from the outside - by television, cinema, writers and journalists, neighbors and acquaintances.So there are specific fears: an impressionable man watched a film about poisonous jellyfish, and something in them impressed him so much that he would now go into the sea with great apprehension, if at all.
Horror films, thrillers, as well as news releases about terrorist attacks, attacks, wars, medical errors - all this forms in us some kind of fear. We ourselves do not have personal experience of the relevant subject matter, but we do have a fear of killer doctors, terrorists, bandits and ghosts. To one degree or another, everyone is afraid of this.
It is very easy to control a person’s consciousness, it’s too easy to convince of the danger that he didn’t meet, he didn’t see.
Fears are more susceptible to people with fine mental organization (in the language of doctors this is called the high excitability of the central nervous system). Even an insignificant external circumstance can have not only a strong panic, but also a resistant phobia.
Effects
Healthy fright passes quickly, does not leave "scars" in the soul and does not return later in nightmares. The normal reaction is to remember the traumatic situation, draw conclusions (learn something), laugh at your reaction and calm down.
But the line between normal and pathological fear is very thin, especially in children and adolescents. If there are personal characteristics of a character, such as secrecy, shyness, fearfulness, then a long or severe fright can provoke the formation of a phobia, speech disorder (stuttering, lack of speech), a delay in psychomotor development.
In adults, the negative effects of fear are not so common, and in most cases the pathological state of mind associated with fear, they have all the same distant "childish" roots.
A person himself may not remember that such a thing happened many years ago at a tender age, but his brain remembers and uses the ligament formed then between the object and the appearance of panic.
From the point of view of psychosomatics, fear is a destructive emotion, especially if it is chronic. That he becomes the true cause of various diseases. Diseases of the heart and vessels, the musculoskeletal system, dermatological diseases, and autoimmune diseases are most often associated with fears. How can fear cause a real disease? Yes, very simple.
Above, the mechanism of fear was described at a physiological level. If the fear is healthy, then the psychological state quickly stabilizes, adrenaline is removed from the body, blood circulation is restored and evenly distributed between the internal organs, skin, muscles.
If fear is almost always present in a person’s life, the reverse development of mobilization processes is not fully or does not occur at all.
Adrenaline does not have time to leave the body, its new emissions provoke high levels of stress hormones. This causes problems with the production of sex hormones (the connection between them has been proven and is beyond doubt). For a child, this is fraught with violations of puberty, growth, development. For adult men and women - psychogenic infertility and a variety of reproductive health problems.
Chronic fear causes muscle clamps. We remember that when frightened, the blood rushes to the muscle tissue and flows from the internal organs, the distribution of blood flow changes. If this happens constantly, the muscles are in tension. This leads to a variety of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, the nervous system, and insufficient blood supply to the internal organs during periods of fear lead to the development of chronic diseases.
When the psychological problem “emerged” on the somatic level, it is no longer a signal, but a desperate cry of the body, asking for urgent help.
But without correction of the psychological background neither pills, nor potions, nor operations will give the desired effect. Psychosomatic illness will persist to return.
The risks of getting a serious psychiatric diagnosis in timid people are always several times higher. Fear that a person cannot control leads to neurosis, phobias at any unfavorable moment can progress and transform into schizophrenia, manic disorder. People who are habitually afraid of something are more likely to suffer from clinical depression.
Pathological fear at the level of a phobia and at all forces a person to perform not quite logical actions, to change his life “for the sake of” his weakness.
If people fear to cross the streets, they build routes to avoid this action. If there are no such routes, they can refuse to go somewhere. Agoraphobes often cannot make purchases in large stores, with a phobia of sharp objects, people avoid using knives and forks, with social phobia they often refuse to visit work, public transport, leave the house, and when they fear water, people start to avoid hygienic procedures and why may lead, no need to explain.
Leaving from a dangerous situation, as it seems to be a fob, is, in fact, a departure from one’s own life.
It is the fears that do not allow us to become what we want, to do what we love, to travel, to communicate with a large number of people, to start animals, to reach heights in creativity, to become smarter, more beautiful, better, more successful. They do not allow us to live in such a way that in old age there is nothing to regret. And is this not a reason to think about how to get rid of your own fears?
Treatment
Independently fight with fear is possible only in the case when it is not pathological. In all other cases, it is impossible to do without the help of a psychotherapist. Since there are many reasons that can cause fear in a person, there are enough ways to deal with the problem.
Pedagogical methods
Teachers, educators, and parents are more responsible for the preventive mission, but it should start from there. If adults create for the child an environment in which everything is clear and simple, then the likelihood of an irrational panic fear is minimal. No matter what the child does, he must be prepared for this, this applies to games and learning. New requirements, new information, if there was no preparation, can provoke fear.
The fob’s parents usually make two mistakes - either they overprotect the child, suggesting that the world is full of dangers, or they give him too little attention, love and participation.
In both cases, a very fertile ground is created for the development of not only anxiety disorder, but also a more serious mental illness.
Russian scientist Ivan Sechenov pointed to the need to raise the will in children from an early age. It is she who, according to the physiologist, will give the opportunity to "perform feats despite fears." And Ivan Turgenev argued that, apart from will, the main means of fighting cowardice is a sense of duty.
For teenagers and children, it is important to understand that they are “insured”.
And then it is important to open the truth and report that there was no insurance and everything was managed to be done independently. So kids are taught to ride a bike. While the parental hands are holding the vehicle, the child is driving quite confidently. But once he discovers that the bike is no longer held, it invariably falls or is frightened. And this is the best time to report that they had not held him before either, and he rode all this time himself. This approach can be applied at any age in any situation.
Addiction to hazards
Adult you or a child, but your psyche is arranged in such a way that it can adapt to any circumstances. Please note that children living in a war zone or in border areas are not at all afraid of the sounds of gunfire, the roar of airplanes, and adults in this situation get used to living more or less adequately.
This does not mean that you can eradicate fear by complete immersion in a dangerous situation. But in 50% of cases it succeeds, on which one of the in vivo psychiatry treatment methods is based.
In practice, this means that you can pick up your key to any fear. If a child is desperately afraid to swim, give him to the section in which an experienced trainer works - with insurance, and then without her, your child will surely float, and fear with each subsequent exercise will decrease, become dull, and be perceived by the brain less acutely. But do not throw the child into the water from the boat according to the principle - “if you want to live, you will swim out”.
This is the right way to form a mental disorder.
With a strong fear of the darkness, you can practice drawing with a light pen (by the light of the drawing it will not work), and gradually the darkness from the enemy for you or your child will turn into a companion and like-minded person. If you are afraid of heights, visit the amusement park more often and ride those that imply a high lift, this will help you adapt faster and the altitude will stop causing horror.
It should be understood that courage in a person cannot be developed either by this method or by others. But to make the perception of fear less tangible is quite possible.
Psychotherapy
People with irrational and prolonged fears, panic attacks, and uncontrollable attacks of horror need treatment and a psychotherapist or psychiatrist. The doctor helps the patient to get rid of the wrong settings that lead to non-existent, imaginary fears. This is well helped by the method of cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy. It involves the identification of all the traumatic circumstances and objects, the work on changing attitudes (sometimes NLP and hypnosis are used), and then they begin to gradually adapt the person to the circumstances that previously frightened him.
At the same time, relaxation is taught, and here meditation, breathing exercises and aromatherapy come to the rescue.
Among the therapeutic approaches for non-launched and shallow phobias, a desensitization method can be used. With him, a person immediately begins to accustom to what he fears. If there is a fear to ride the bus, first ask to come to the stop and sit there. Realizing that this is not scary, you can go into the cabin and immediately get out, and the next day, go in and drive through the stop. In most cases, the method needs constant follow-up of the patient at the very beginning of the therapy - someone he trusts, or the doctor should do everything with him, and then discuss the situation together, emphasizing that nothing terrible has happened.
Distraction method is quite effective.
The psychotherapist creates a "dangerous situation" (sometimes under hypnosis). Describes it, asks the patient to tell what is happening with him. And when a person's emotions reach a peak, the doctor asks to see, and who is now standing side by side in the created illusion (in the bus, for example). If it is a woman, what is she wearing? Is she beautiful? What is in her hands? If this is a man, does he inspire confidence? Is he young? Does he have a beard? Distraction allows you to focus point of attention from a panic to a new object. Even if this fails immediately, the results gradually appear.
Subsequently, people can use this technique themselves, without hypnotic effects. He began to worry, worry - pay attention to the small details of something that has nothing to do with the object of fright.
Psychotherapy is today considered the most effective way to cope with pathological fears.
Sometimes, if the condition is complicated by concomitant mental problems, medication support may be required.
Medicines
But there is no cure for fear. He simply does not.Tranquilizers, which were considered effective not so long ago, cause chemical dependence, moreover, they only mask the manifestations of fear, dulling the perception of the whole as a whole, and do not solve the problem. After the abolition of tranquilizers usually phobias return.
Significantly better results show antidepressants that can be prescribed simultaneously with psychotherapy (there will be no effect apart from them). In case of sleep disturbance, hypnotic drugs are recommended, and in case of neurosis or neurotic state - sedative, sedatives are recommended.
But it is better not to rely on pills and injections to overcome fears - they are considered to be auxiliary methods, not the main ones.
The main thing in treatment is diligence, diligence, big and strong motivation. Without cooperation with the doctor, without compliance with all his recommendations to achieve the desired effect will not work.
Prevention
Prevention of the development of pathological fears should be dealt with since childhood. If you want to grow a person who does not become a hostage of phobias, use the advice of psychologists:
- if a child is afraid of something, do not laugh at it, even if it is really absurd fright, treat your experiences with respect and be prepared to listen seriously and to make out the frightening situation together;
- give the child more time, warmth, and affection - this will be his “insurance”, with which it is easier to deal with frightening situations;
- Build relationships with the child so that the child trusts you, can at any time, even in the middle of the night, come and tell your nightmare, share fright;
- do not artificially create situations in which a child may experience a panic attack (do not teach him to swim, throwing into the water in spite of protests, do not force him to stroke a hamster if rodents scare him);
- Constantly overcome your fears, make it so that the child sees the result - this is a great vivid example and the correct installation of the child for the future - “I can do everything”.
It is strictly forbidden:
- blame the child for fearing him, calling him a coward, a weakling, provoking any actions, scolding and punishing the child for his fear;
- to pretend that nothing has happened - ignoring a child's phobia does not solve the problem, but drives it deeper, which then almost always results in the formation of a stable phobia;
- To set an example for yourself: “I’m not afraid, Dad is not afraid, and you shouldn’t be afraid!” - this doesn’t work at all;
- to assert that someone died due to illness, the child’s psyche quickly connects the notion of “getting sick” and “death”, which leads to the development of anxiety in situations where someone is sick or is ill, and also out of for fear of being infected with something;
- to take the child in farewell to the dead, to funeral ceremonies before adolescence;
- coming up with “horror stories” - Babai will come, if you don’t eat, you will die of exhaustion, if you don’t go to sleep, the Gray Wolf will take it, etc .;
- to overprotect the child, to prohibit him from contact with the world, to limit his independence;
- Watch horror movies before reaching the age of 16-17.
And most importantly - do not hesitate to ask for the help of specialists, if you can’t cope with children's fears on your own.
There are a great many methods - from art therapy to physical therapy, which will help to overcome any nightmares under the control of an experienced psychologist or psychotherapist. If you do not promptly contact a specialist, the consequences of running anxiety disorder will be very negative.
On what fear is, see below.