Fears are different. What one person is afraid of may seem ridiculous and ridiculous to another, but this does not detract from the fact of the presence of fear. The list of phobias, known to science and sufficiently studied by modern psychiatry, has more than a hundred names, and for each of them lies a certain fear that can change a person’s life beyond recognition.
Subject species
Phobia is called a symptom that is an inexplicable and irrational fear of something. Man usually cannot control this emotion. Phobias are very stable, they can haunt a person from childhood to old age. People suffering from these or other phobic mental disorders, by all means try to avoid situations and circumstances that cause them great anxiety. As a rule, they are well aware of the far-fetchedness and even the absurdity of their fear, but they cannot do anything with it.
Phobias manifest high levels of anxiety, loss of self-control, panic attacks, and sometimes loss of consciousness. Understanding that a person cannot cope with his horror, he often decides to leave a potentially dangerous situation. So people become voluntary hermits (with fear of the street, fear of leaving the house), social phobias (with fear of communicating with people, fear of being misunderstood, unaccepted). People with some phobias cannot create families, find a normal job, travel, enjoy life. Fears significantly limit human capabilities.
It is believed that some types of phobic disorders have almost 70% of the world's population, while specific phobias occur in about 8-10% of cases. Most of those suffering from phobias live, according to statistics, in Europe and the Western world, only 4% are Asians, Africans and Latin Americans. Women according to existing WHO data tend to suffer from different nightmares about twice as often as men.
The vast majority of phobias start for the first time at the age of onset of puberty, that is, from the age of 10. With age, the number of patients with phobias decreases.
Psychiatrists, speaking of phobias, imply pathological manifestation of the reaction of fear to stimuli. It is believed that coping with phobias is much easier at the initial stage. Long, complex and neglected nightmares are rarely curable. Psychoanalysts mean by phobia a state of obsessive neurosis, in which the anxiety begins to actually control the behavior and thinking of the patient.
Not every fear can be considered a diagnosis. Mental impairment is only talked about. if persistent irrational horror is present for more than half a year, and its manifestations significantly limit human activity.
The Psychiatric Encyclopedic Dictionary, compiled by a group of authors (Y. A. Stoimenov, M. Y. Stoimenova, P. Y. Koyevoy, and others), has several dozen phobias classified by alphabet. For more convenience, we have divided these fears by topic.
Health and limited space
The list of these fears is very impressive, because in a varying degree, all people experience their health and being in space. Here are the main fears that relate to health, as well as spatial phobias.
Ablutophobia - this is the fear of washing, bathing, cleaning, washing. At the same time, a person may not be afraid of open reservoirs, but any hygienic procedures are extremely unpleasant for him, and sometimes even cause permanent rejection.
- Agirophobia (dromophobia) - the horror of the streets. Some fear the prospect of crossing a wide street with a mass of cars, while others are pathologically afraid of the narrow and quiet village streets.
- Agoraphobia - fear of open spaces, squares, crowds of people. In severe form can manifest a complete refusal to leave the limits of his apartment.
- Aichmophobia - pathological irrational horror of sharp objects, knives, fear of injury. Aichmophobes usually try to avoid kitchen sharp objects to the extent that they refuse to cook, buying ready-to-cook foods, and in 90% of cases they are afraid to cut their nails.
- Acliophobia - A rare disorder, accompanied by unwarranted fear of deafness. People with such a phobia avoid loud sounds, try to be very attentive to the health of their ears.
If they hear an explosion sound or another sudden loud sound, they may experience a strong sense of panic.
- Aknefobiya - A strong fear of acne, acne. Often accompanied by obsessive-compulsive disorder, in which a person constantly tries to wipe his hands and face with clean wipes.
- Apopathobia - unexplained fear of visiting toilets. Some people show only fear of going into public toilets, others (rarely) - and individual toilets.
- Apoplexyphobia - fear of stroke. It is noteworthy that mainly young and healthy people who have minimal cerebral hemorrhage risks suffer from phobia. It develops most often in people who have seen the effects of strokes from loved ones, friends.
- Ataksiofobiya - Pathological strong horror from the prospect of losing balance and the ability to coordinate their movements. Often occurs in professional athletes, circus performers, in people whose professional activities are connected with the need to keep balance.
Often, axiophobes cannot take alcohol in any quantities for fear of losing their balance.
- Autosisophobia (Misophobia) - fear of pollution of your body, your skin, fear of being dirty and contracting dangerous diseases. This fear is usually closely associated with depression. In a severe form of disorder, a person limits tactile contact with people and objects to a minimum, or tries not to touch anything at all.
- Aerophobia - fear of moving on aircraft, being in the cabin, as well as fear of a draft. A very common type of fear, in severe form, can manifest itself by a complete rejection of air transport.
- Aeroemphasis phobia - unexplained fear of the development of decompression sickness. Often found in professional divers, divers, pilots, astronauts. But anyone can develop, and even an understanding that decompression in everyday life does not threaten anyone, cannot guarantee the absence of the development of a corresponding nightmare.
Basophobia - fear of walking without support. It may manifest fear in the absence of a railing, handrails, as well as the hands of a friend, comrade, partner, close. People with such a disorder are calm only if they have physical support while moving (at least a cane or walkers).
At the same time, there are no objective reasons for fear - the legs and joints, the spine and the muscular corset of the basiophobe are completely healthy.
Bacteriophobia (bacillophobia) - This is a strong fear of microbes, bacteria, fear of becoming a victim of bacterial infection. It manifests itself as an obsessive idea to create a sterile space around. Panic attacks can occur at any time if they fall into the familiar habitat of a foreign object, person, etc.as they can be sources of pathogens.
- Blaptophobia - fear of harm, injury to someone or something. Often develops on the background of depression. Blaptophobic are hesitant, they are restless because their actions can be dangerous for others, and this concern can be manifested by tremors, hysterics, cramps, spasms of the respiratory muscles and rapid heartbeat.
- Bromhydrophobia - fear that others will notice the smell of sweat or unpleasant body odor. The disease is also called the disease of excess purity. Often this form of fear is found in people with extremely low self-esteem. The very fact of self-sweating causes panic, there is a need to immediately get into the shower, or at least use a deodorant. Bromhydrophobes are often abused by perfume.
- Vaccinophobia - fear of vaccinations and possible complications from them. Relatively young phobia, which fell into the list of fears relatively recently. It can be manifested either by fear only before a certain type of vaccine, for example, before “live” vaccines, or it can be associated with all the prophylactic vaccines without exception.
Venerophobia - fear of contracting a venereal disease. It can manifest fear of unprotected sexual intercourse even with a regular partner, or it can manifest itself in the belief that the disease already exists, while the majority of venerophobes are afraid to go to a doctor - they are hyper-revealing.
With the early development of a violation, a person may refuse to have intimate relationships altogether, considering them to be a threat to their own life.
Verminophobia - fear of small worms, parasites, microbes, infection. A rather extensive list of fears on which the producers of antibacterial soap and sterile home wipes earn well. There are even special computer keyboards for verminfobs. The basis of the fear of becoming infected and dying is usually the negative experience of the past (in childhood a person had an infection and is now afraid of repetition).
Vertimphobia (dinophobia) - fear of dizziness and loss of balance. Often develops in people who really have problems with the health of the heart, blood vessels, vestibular apparatus, the auditory nerve. At the same time, a person perceives vertigo as signs of a dangerous disease and begins to fear the symptoms themselves.
Halitophobia - fear of bad breath. A person is very afraid that his breath will seem smelly to others. Not always for such fears there is even the slightest reason. Fear quickly turns into anxiety disorder, into obsessive-compulsive neurosis, in which a person constantly, as an institution, performs the same program of actions aimed at refreshing his breathing and checking his freshness.
- Hemophobia (hematophobia) - fear of blood (one's own or someone else's). Most often develops after injuries or medical intervention associated with blood loss in childhood. At the same time, the event itself can safely be forgotten due to the prescription of years, but fear is imprinted tightly in the subconscious. It manifests itself sharply, sharply - with nausea, dizziness, tremor, obsessive smell of blood, noise in the ears, loss of consciousness may occur.
More peculiar to women than men.
- Hydrosophobia - fear of sweating. Usually, a person is afraid of sweating for two reasons - either for fear of catching a cold or for fear of starting to smell badly, which others will notice. Usually, hydrosophobes are very worried when they see other people who sweat, and therefore usually they try not to go to the gyms, stadiums, baths.
Gymnophobia - fear of nudity. Patients fear that someone will see them naked. In some cases, someone else’s nudity is also alarming, and therefore her hymnophobes are also avoided.Most often, the violation is associated with negative experiences experienced in childhood, as well as low self-esteem, when a person considers his body to be shameful, ugly.
Dentophobia - fear of dentists, dentists. According to experts, every third inhabitant of the planet suffers from this kind of fear. Dentophobes turn to the dentist only as a last resort, and therefore they usually have problems with dental health.
Dermatopathobia - fear of contracting skin ailments. Fear of the prospect of becoming a patient of a dermatologist makes a person use soap, detergents and disinfectants more often. And it is their frequent use that causes skin problems, which intensifies a person’s panic. It turns out a vicious circle, to get out of which is difficult.
Iatrophobia (iatrophobia) - fear of doctors, nurses, orderlies, and anyone wearing a white coat. It may manifest itself in the form of refusal to visit the clinic, to be tested.
In severe cases, the person generally refuses any treatment, including the one he needs for life reasons.
Iophobia - fear of poison, fear of being poisoned. A person can be afraid not only of food poisoning or drugs, but also poisons that can get on the skin and under it with insect bites, with handshakes. Iophob food preferences are usually poor - he eats only limited food groups, he cannot be fed anything outside the house if he doesn’t know who was preparing the treat and what. At home, a person with this disorder can always have an impressive collection of insecticide products. Signs of poisoning people may feel regularly.
- Carcinophobia - fear of getting cancer, cancer. Most often develops in people aged 40+. The reasons may lie in the example of relatives, and in the perception of the danger and incurability of cancer in general. Often the fear of death and torment from cancer develops against the background of an already existing depression, as well as other mental pathologies.
- Cardiopathobia - fear of heart disease, seizures. It develops more often in people in whose family there have been deaths from heart disease. It is also believed that the likelihood of developing such fear increases with age. To a greater extent it is subject to pensioners, who often visit doctors, and pass tests.
Kenophobia - fear of large empty spaces, cinema halls, theaters, foyer and halls. In this case, fear is caused not so much by large spaces, as by the fact that they are not filled with anything, and therefore the brain of kenophobe instantly "draws" all sorts of dangers that can be covered in a large hall.
Fear is manifested by panic attacks and attacks.
Claustrophobia - pathological fear of confined space and the prospects of being in a dense crowd. Claustrophobes leave the doors open, avoid moving on an elevator, often afraid of train cars and cabin airplanes.
Klimakofobiya - fear of stairs, the need to walk on them. At the same time, the staircase itself and the process of walking on it can cause horror. The causes of the pathological condition are not obvious, medicine, they are still not completely clear. The disorder is rare.
Copophobia - fear of overworking. Often develops in adults and well-established in the lives of men and women who have heard of the dangers of overwork or have themselves experienced the effects of chronic fatigue. Disorder manifests itself atypically for phobias - a person does not try to avoid affairs and responsibility, and even vice versa - tries to load himself more. And the more he takes on himself, the stronger the level of anxiety and worries about possible fatigue.
- Coprophobia - fear of feces. Cause an attack of panic and disgust can not only the type of feces (his, others, dog, etc.e.), but also talk about defecation, and sometimes even advertising laxatives. A person's hands, lips begin to tremble, dizziness appears, he may lose consciousness.
In severe cases, the coprophob may refuse to empty the intestines, which leads to obstruction and requires urgent surgical treatment.
Lalophobia - Fear of stuttering. Caused by the fear of becoming a laughing stock in the eyes of others. It occurs not only in people who suffer from stuttering, but also in those who have never stuttered, but are very afraid that it is they who can have a sudden and inexplicable stutter.
- Maniophobia - fear of becoming mentally ill. Maniofobov literally pursues an obsessive thought that they will definitely go crazy one day, and therefore they regularly find symptoms of various mental disorders. The “trap” is that when a phobia progresses, a person really goes crazy. Therefore, the condition necessarily needs to be treated, otherwise it is a stone's throw to the real madness.
- Menophobia - fear of menstruation. It can be combined with hemophobia (fear of blood), and can be an isolated fear, for example, a woman is afraid of unpleasant feelings during the period of menstrual bleeding.
Misophobia (germphobia) - fear of contracting infections. Mysophobes are afraid to touch foreign objects, to contact people who do not inspire confidence in them. They often avoid public transport, public baths and any places in which theoretically they can become infected with any infectious disease.
Nosophobia - fear of getting sick. This concept includes numerous fears of specific diseases (lissophobia — fear of schizophrenia, leroprophobia — fear of leprosy, speedophobia — fear of HIV infection, etc.), as well as a general fear of becoming ill. Such people are concerned about their health, hygiene, nutrition, read a lot of information about the symptoms of diseases and even find the lion’s share of themselves.
The classic nosophobe is a regular at the polyclinic, it constantly seems to him that he is ill, but the doctors are simply not well prepared to recognize his illness.
- Nosocomofobia - pathological fear of hospitals, hospitals, hospitals. People with such a disorder, on the contrary, cannot be lured into the hospital, which in itself is dangerous, because in the absence of diagnostics and timely detection of many diseases, a person is in grave danger. Most often manifested in childhood. In adults, it has a severe course.
- Onanophobia - horror of the possible consequences of masturbation. It develops more often in adolescents; it may have a severe course, in which a person generally refuses to build up his full intimate life. Usually associated with the terrible stories about the dangers of onanism (often inconsistent with reality), which adults frighten adolescents. Most often, this form of fear affects boys.
Patroyophobia - fear of hereditary diseases. Usually it develops among those who really have patients in the family, as well as people who have very difficult relations with their relatives: they begin to fear that they will show negative features and that relations with their own children will also be difficult. If left untreated, fear can turn into paranoid disorder.
- Parurez - fear of urinating in humans. A separate disease and disorder is not considered, but often accompanies a variety of disturbing social phobias. More common in men.
- Peladophobia - fear of baldness. It can develop in both men and women. Manifested in the fact that people begin to rapidly avoid contact with balds, because in their presence they begin to experience a strong emotion.
Any hints of baldness as a phenomenon cause rapid breathing, loss of self-control.
Petrophobia - fear of inadvertently farting at people.Fear can reach such a strength that a person stops visiting public places, fears of standing in a queue at the store, since uncontrolled emission of intestinal gases, according to a pettophobe, can arise at any moment.
- Tokofobiya - fear of childbirth. Most often, tokofobami are women, but there are also representatives of the stronger sex, who suffer from bouts of fear and panic at the mention of pregnancy and childbirth. Fear can be multifaceted - it is the fear of not becoming a good parent, and the fear of pain in childbirth, and the negative experience of abortion in the past, and even the fear of losing a good figure after childbirth. In severe form, the fear of childbirth makes a woman voluntarily refuse to continue the race.
- Topophobia - fear of remaining in some room alone. We are talking about a particular room or type of premises (basements, attics, storerooms) or all the rooms without exception (rarely). Such a person is very important that someone was with him constantly, even if it is a cat or a dog.
- Traumaphobia - fear of injury. It occurs with hypertrophied self-preservation instinct. Traumatophobia in the past often suffered injuries, usually it happens in childhood. Disorder is manifested in heightened caution, in the use of personal protective equipment, even in circumstances in which it seems inappropriate.
- Tremphobia - fear of trembling, tremor. It is often a symptom of other phobic disorders, when hands or lips begin to tremble in a state of excitement in a person.
Trying to hide fear, a person is more worried, which invariably leads to increased trembling.
- Trypanophobia - fear of injections, needles, syringes, piercings, etc. Any punctures on the body (even as a possible event) cause extreme excitement in trypanophobe, deprive it of rest and sleep, in severe form the disorder can be accompanied by a complete refusal of testing, treatment .
- Tuberculosis (phthisiophobia) - fear of contracting tuberculosis. It usually develops in impressionable people after becoming familiar with the symptoms and ways of transmission of this dangerous disease. They refuse to shake hands, try to avoid being in the same room with those who cough (regardless of the causes of cough), often wash their hands, and make inhalations at home. In severe form, avoid contact with strangers and try not to take up the door handles anywhere.
- Tunnelephobia - fear of overcoming the tunnel. It is a form of spatial phobia. It can manifest itself both in a complete refusal to fall into any tunnels, and in a refusal to overcome them alone, without accompanying ones.
- Pharmacophobia - fear of taking medications. Often bordered by the fear of doctors, with fears of possible poisoning. Sometimes it develops as a long-term memory for the side effects of medication in childhood, but may be due to negative information from the outside (reports of counterfeit drugs, dangerous falsifications, etc.).
Phyriophobia - fear of pediculosis, lice. A person is so afraid of contracting pediculosis that he tries to avoid anyone who not only scratches his head, but also touches his hair. Frequently, phthyriophobes complain of itchy scalp, taking it for the symptoms of lice, but the real danger of trying to use different chemicals and insecticides on their own, with which people suffering from this disorder try to get rid of a non-existent problem.
- Emetofobiya - fear of vomiting. One of the most neglected phobias, although it affects about half of the people on the planet. May manifest fear of their own vomiting in humans, as well as the fear that a person may experience when contemplating someone else's vomiting.
- Epistaxophobia - fear of nosebleeds. To control such a condition as epistaxis (nosebleeds) is really impossible.And if a person is prone to frequent nosebleeds, then he may develop such a phobia.
Fear of blood from the nose is rarely manifested in the absence of reasons and prerequisites for such bleeding.
- Erythrophobia - fear of blushing. Some people blush when they lie, some - during heavy excitement. Erythrophobic is afraid that redness for any reason will find him at the wrong time in inappropriate circumstances, when he will be in public.
Natural phenomena, flora and fauna
Fears of natural phenomena and representatives of the animal and plant worlds are among the most ancient. They were formed at the dawn of humanity and will remain for a long time as manifestations of the instinct of self-preservation. But for some, these fears overstep the limits of reasonable ones and lead to loss of control over themselves every time a person encounters what he fears.
Such fears do not always arise as a result of negative personal experience. Often the reason lies in the age-old "memory of ancestors." Such fears are often inherited. Here is a list of the most common phobias of this type:
- Ilurophobia (felinophobia) - fear of cats;
- acarophobia - pathological horror before ticks and their bites;
- anemophobia - fear of a storm, possible spontaneous destruction;
- anthophobia - fear of flowers (both wild and in pots);
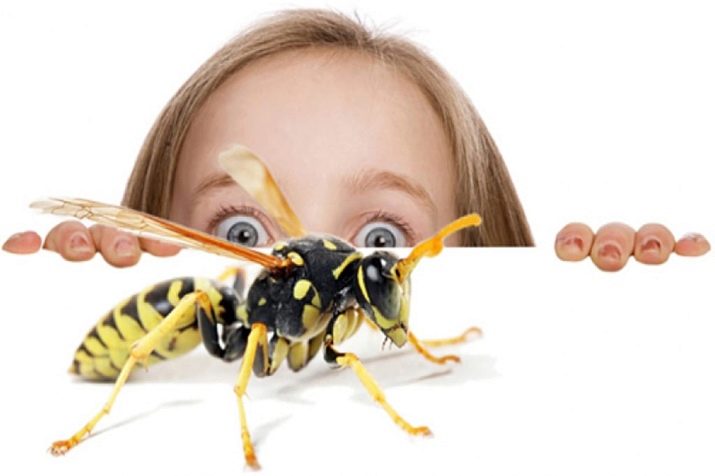
- apiphobia - fear of bees, wasps and their bites;
- arachnophobia - fear of spiders;
- astrophobia - fear of stars, starry sky, starry space;
- brontophobia - fear of thunder;
- galeophobia - pathological fear of sharks;
- heliophobia - fear of being in the open sun;
- herpetophobia - fear of snakes and reptiles;
- gilofobiya - fear of getting lost in the forest;
- zoophobia - fear of animals in the broad sense of the word (many of the terms listed in the list are varieties of zoophobia, its particular cases);
- zemmyphobia - fear of moles;
- insectophobia (entomophobia) - fear of insects;
- keraunophobia - fear of lightning flashes;
- film phobia - pathological fear of dogs of all sizes and breeds;
- myrmekophobia - fear of ants;
- musophobia (or surefobiya) - fear of mice, rats, other rodents;
- nyctophobia - fear of night time, darkness.
- ombrofobiya - fear of getting wet in the rain;
- ornithophobia - fear of birds and their feathers;
- pyrophobia - fear of fire;
- psycho phobia - fear of cold;
- radiophobia - fear of radiation;
- ranidophobia - fear of frogs;
- thalassophobia - fear of the sea (the reservoir itself and the process of bathing in it);
- uranophobia - fear to look at the sky;
- chiroptophobia - fear of bats;
- equinophobia - fear of horses.
Interaction with people and age fears
Social fears occupy an honorable place in terms of prevalence. They are usually associated with the need to build social contacts, as well as age-related changes in the psyche. These include:
- agraphobia - fear of sexual harassment;
- androphobia - pathological fear of men;
- anthropophobia - fear of the company of people;
- autoyobia - fear of loneliness;
- gamophobia - fear of marriage;
- haptophobia - fear of someone else's touch, the need to touch someone;
- helotophobia - unreasonable strong fear of becoming an object of ridicule;
- genophobia (koitofobiya) - fear of sex;
- gerontophobia - fear of old age;
- heterophobia - unfounded fear of the opposite sex;
- gynophobia - pathological fear of women;
- gravidophobia - a rare horror for pregnant women, fear of the prospect of meeting a pregnant woman;
- demophobia (okhlofobiya) - the horror of a gathering of people, a crowd, a gathering;
- logophobia - strong irrational fear of the process of conversation in the presence of other people;
- paralyphobia - fear that any erroneous action of a person can harm his relatives, friends, people dear to him;
- pediophobia - irrational horror for children;
- scopofobia - fear that other people will look at you;
- social phobia - fear of society, public condemnation, failure;
- transphobia - pathological fear of transgender people, acute rejection of signs of transsexuality;
- philophobia - fear of falling in love, feeling affection for someone;
- ephebifobia - pathological fear of adolescents.
Food
Such phobias are common mental disorders, they, according to statistics, affects up to 12% of the population in a more or less severe degree. Here are some of these phobias:
- wine phobia - pathological fear of drinking wine (and sometimes other alcoholic beverages);
- sitophobia – fear of eating in general;
- trichophobia - the horror of the hair that got into the food;
- phagophobia - fear of swallowing food, choking in the process of swallowing;
- hemophobia - fear of possible chemical additives in food.
Mystical
Both men and women and children are subject to this group of phobias. Everything that has a mystical color at all times was perceived as something nightmarish, but sometimes fears become strong, irrational and turn into a phobia. Here are a few of these phobias:
- arithmophobia - fear of a certain number, which has a certain mystical significance for a particular person;
- hierophobia - panic in front of objects related to any religious cult;
- hexacosiaohexagontahexaphobia - a fright before the “devilish” number 666;
- demonophobia (satanophobia) - fear of demons, the devil;
- parasweed cataphobia (triskaidecaphobia) - fear of the number 13;
- spectrophobia - pathological fright before spirits, ghosts, ghosts;
- theophobia - fear of God, his possible interference in the affairs of man, the divine punishment;
- coolrophobia - fear of the image of a clown.
Atypical
There are also fears that conditionally distinguish atypical in the group. This only means that they are quite rare, and the causes of such phobic disorders are usually not established:
- acriophobia - fear not to understand the meaning of the read information;
- hippopotomonstroseskipedalofobiya - compulsive horror from long words;
- dorophobia - panic fear to make gifts and receive gifts from others;
- dextraphobia - obsessive fear of all items located at the current time to the right of the person;
- decidophobia - fright before making a decision;
- imodjifobiya - panic that you will be misunderstood when you use emoticons in correspondence;
- retterophobia - fear of being wrong in writing a word, not to notice the autochange function;
- self-phobia - fear of unsuccessful self, which will cause the condemnation of others;
- hirophobia - inexplicable horror inappropriate to laugh in an environment that does not predispose to this, for example, at a funeral;
- chronophobia - the horror of time, its course.
Top 10 most common fears
Nicothobia - fear of the dark, night time. This is the most common fear of the modern world and it occurs in people of different ages, sex, education and social status. Up to 80% of children suffer from nyctophobia, and in adults the prevalence of phobia is about 9-10%.
Acrophobia - panic fear of heights. It affects up to 8% of the inhabitants of the planet. Any stay at the height, flight, the need to look out the window from the upper floors give rise to the strongest unconscious fear of falling. And the fall is quite possible, because at the time of a panic attack a person really loses the ability to control himself and his actions.
- Aerophobia - fear of moving by air, flying on an airplane. Up to 7% of people suffer from this disorder. May be accompanied by an additional fear, for example, thanatophobia (fear of death).
- Claustrophobia - fear of confined space. It occurs in 5-6% of people in varying degrees. Patients try to avoid traveling in the elevator, do not close the doors, windows. Even a cramped tie or a shower can cause a panic attack on some.
- Aquaphobia - the fear of water. It occurs in 50% of people who survived tragedies on water, catastrophes, flooding, etc. Without preliminary predisposing causes, it occurs in 3% of people on Earth.
- Ophidiophobia - the horror of snakes. Pathological fear of snakes is found in 3% of people. Some are afraid only at the moment of contemplation of a reptile, some are capable of “inventing” him and suffer from the obsessive thought that there may well be a snake in their home at the moment.
- Hemato phobia - fear of blood in its pathological variant occurs in 2% of the inhabitants of the planet. In almost half of the cases, terrible bloody films seen in childhood, as well as careless manipulations of health workers are guilty of the development of fear.
- Tanatophobia - the horror of his own death and the death of others. Usually found in religious people, after a not too successful period of midlife crisis. In children is rare.
- Glossophobia - pathological fear of public speaking. It happens in mild form in 90% of the inhabitants of the planet, but in the form of the disease goes in 3%.
Jeremophobia - fear of deep silence. May be accompanied by sound hallucinations, a feeling of irrational fear, a desire to run. It occurs in about 1.5-2% of earthlings, most often in residents of large cities, who are used to noise, even at night.
List of funny phobias
- Gnosiofobiya - pathological fear of obtaining knowledge. Usually residents of megacities suffer from such a phobia, as well as children who grew up in uneducated tribes, and Mowgli children.
- Kumpunofobiya - fear of buttons. Very rare phobia, which occurs only in one case for 70 thousand people. Manifested in the fact that a person diligently avoids such accessories on clothing.
- Penteraphobia - pathological fear of mother in law. No matter how anecdotes it may sound, there are men who really cannot communicate with their mother-in-law without the death of terror in their souls and panic in their eyes. Exactly the same term is called the fear of mother-in-law in women.
- Pogonophobia - fear of a beard. It manifests itself in the pursuit of a cattle phobia carefully avoids any contact with those who have a long beard. If you can not avoid communication, it provokes a panic attack.
- Papaphobia - the pathological fear of the Pope. All in all, only a few cases of intolerable human horror at the mention of the Pope’s name are known, but they are noticed and made the official list of phobias.
- Lacanophobia - fear of vegetables. One type of cucumber or zucchini can trigger a horror attack, panic and dizziness in lacanophobe. Usually, the smell of vegetables for such people is unbearable.
- Nenophobia - fear of the clouds. They change shape, are in motion, and this fact itself is disturbing to the nenophobe.
- Omphalophobia - fear of navels. Omphalophobes are afraid of the navel - they don’t allow anyone to touch this part of the body and try not to touch or look at the navel themselves.
What are celebrities afraid of?
- Peter the Great (Great) suffered from entomophobia - was afraid of many insects, especially cockroaches. He forced to regularly check his chambers for the presence of insects before he had to go there. This fact is widely reflected in the memoirs of his contemporaries.
- Franklin Roosevelt I was terribly afraid of fire, suffered from pyrophobia since childhood, when in 1899 I witnessed a terrible fire. For the night, Roosevelt always left the door open, and the duties of the Secret Service officers included regular fire safety checks at his residence.
- Fearless warrior conqueror Genghis Khan suffered from film phobia - he was afraid of dogs. As a child, he witnessed a Mongolian wolfhound being torn to pieces in a steppe.
- Psychoanalyst Dr. Sigmund Freud suffered from agoraphobia, feared weapons and ferns. The fear of open spaces prevented the elderly Freud from taking walks without pupils.
- North Korean leader Kim Jong Il afraid to fly. Aerophobia with him was so strong that in his political trips he always chose only ground transportation.
- Claustrophobic suffers from Hollywood actress Uma Thurman. On the set of Kill Bill-2, she decided to play herself in a scene where she was buried alive, which she regretted - the horror was so strong that Mind then needed the help of a psychotherapist to continue working on the film.
- The most famous social phobia of our time - mathematician Gregory Perelman. He does not leave home, refuses to participate in conferences, does not give interviews, and also refused to come to Paris and receive a well-deserved award of 1 million euros.
- Emperor Octavian Augustus panicked by thunderstorms. He even built the temple of Jupiter of the God of Thunder to placate the gods, but the fear did not go away.
- Hitler was afraid of dentists, Napoleon - cats and white horses.
On how to deal with phobias and fears, see below.